Visual merchandising strategies for the digital retail environment
The retail industry has changed dramatically in recent years, with digital storefronts becoming as important as physical ones. Visual merchandising, once limited to shop windows and in-store displays, now extends into the virtual realm where customers shop with a few clicks. This shift requires retailers to rethink how they present products online.
Digital visual merchandising blends creative design with data driven decision making in online retail. From product photography to personalised recommendations, these strategies help bridge the gap when customers cannot physically touch products. Well crafted digital displays showcase merchandise and guide the customer journey.
Retailers now treat visual merchandising as an ongoing discipline. Design and data work together to influence outcomes. This approach helps brands stay relevant as retail evolves.
As technology advances, retailers face both challenges and opportunities in digital merchandising. The most effective approaches balance aesthetic appeal with functional navigation. With the right tactics, online retailers can create digital environments that encourage shoppers to make purchases.
Digital Visual Merchandising Fundamentals
Digital visual merchandising focuses on how retailers present products online to attract customers and drive sales. Unlike physical stores, digital merchandising lacks tactile elements but offers advantages in personalisation and using data to inform decisions.
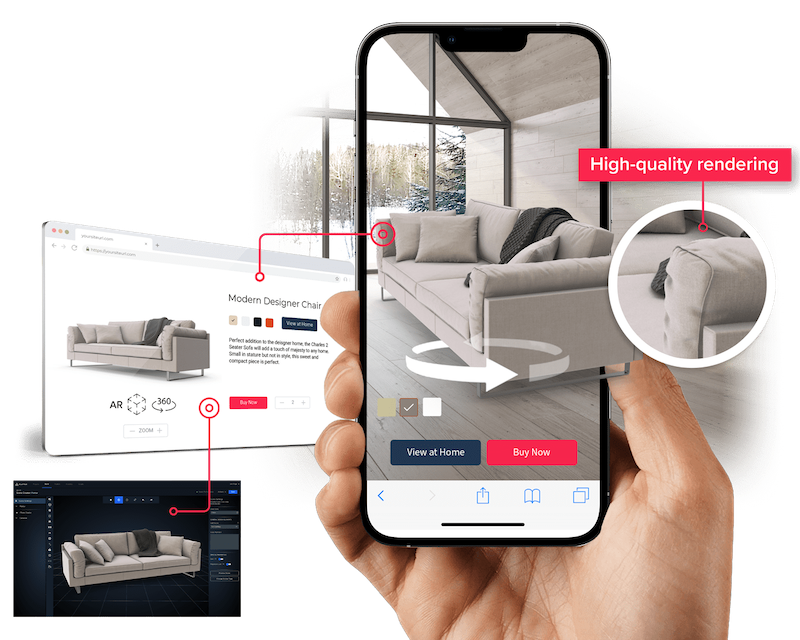
The main difference between physical and digital merchandising is sensory engagement. Physical stores allow customers to touch products in three dimensions. Digital settings must use high-quality visuals and interactive elements. The text-to-video tool helps create product videos from text prompts.
Several traditional merchandising principles work well online. The rule of thirds, colour psychology, and strategic product grouping translate to digital spaces. These guidelines must suit screen-based viewing and various device sizes.
Effective digital merchandising can have an impact on business metrics. Visual presentation may influence conversion rates, though results can differ depending on the retail sector and audience. For accurate measurement, retailers should use analytics tools and A/B testing within their own environments.
AI tools are transforming digital merchandising by automating content creation while keeping brand consistency. Retailers can find more resources in digital merchandising guides.
Product Presentation Techniques That Drive Conversions
High quality product imagery forms the foundation of successful digital merchandising. Images should be sharp, well lit, and show multiple angles. Interactive elements like 360 degree views let shoppers examine details and improve the shopping experience.
Video demonstrations can help customers better understand products by showing them in action. Short videos are increasingly used in digital merchandising to enhance the online shopping experience.
Maintaining a consistent visual language across product categories builds brand recognition and customer trust. The text-to-video tool gives retailers efficient ways to showcase products without expensive photoshoots.
Image Optimisation Best Practices
Technical requirements for optimal product imagery include high resolution, proper colour calibration, and multiple angles. File formats should balance quality with load speed. JPEG is often used for product photography.
Page load speed can influence conversion rates. Visitors tend to prefer fast sites, and slow pages may negatively affect user experience. Retailers should compress images, implement lazy loading, and use content delivery networks for better performance.
Standardised product photography creates a unified shopping experience. This means consistent camera angles, lighting, and image dimensions across categories. Clear guidelines ensure consistency, even with different photographers.
A/B testing helps retailers determine which image styles work best. Tests can focus on variables such as background colour, product angle, and the number of images displayed.
Digital Store Layout and Navigation Design
Category structure shapes intuitive shopping. Retailers should organise products in ways that make sense to customers, not just internal systems. Card sorting exercises with customers reveal natural category groupings.
Visual hierarchy techniques guide customers through digital storefronts. Primary categories need prominent placement, with related items positioned nearby. Colour, size, and positioning create effective hierarchy.
Filtering and sorting mechanisms help customers narrow options based on their needs. Filters should reflect essential product attributes such as size, colour, and price. Faceted navigation showing product counts helps shoppers make faster choices.
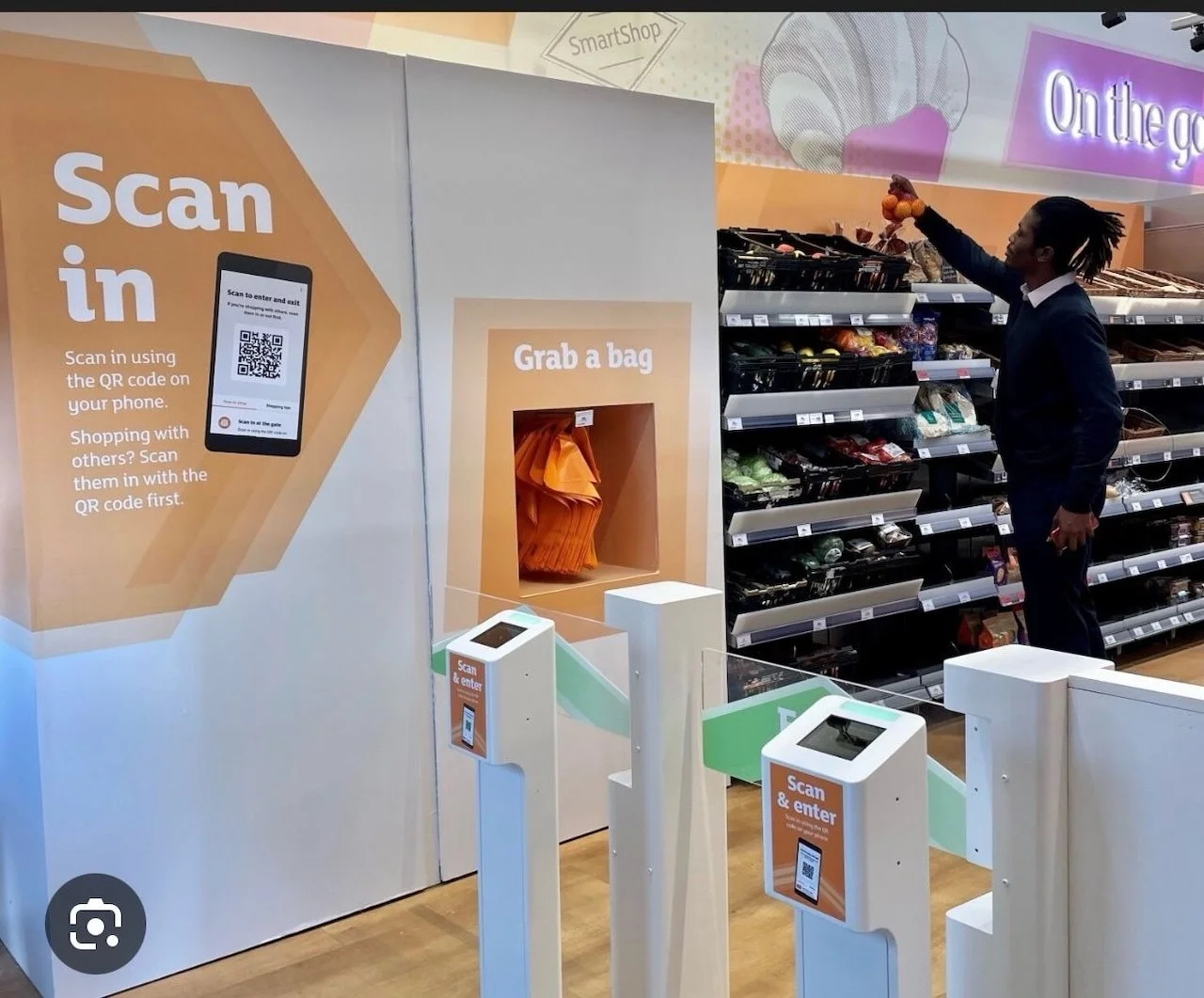
Mobile specific layouts require attention as mobile shopping becomes more common. Heat map analysis can help refine placement based on areas where customers focus most. Products in high-attention areas often gain more engagement.
Personalised Visual Merchandising
Dynamic product displays that adjust according to user behaviour may increase engagement. The impact depends on retail sector, execution quality, and audience expectations. Retailers should measure improvements with analytics and controlled testing.
Segmentation allows tailored merchandising for different groups. Common segments include new versus returning customers, price sensitive shoppers versus luxury buyers, and seasonal shoppers.
Personalisation works best when combining algorithms with human curation. Algorithms find patterns quickly, while merchandisers keep brand consistency. Both approaches together create better results.
Privacy remains a top priority. Retailers should clearly state data practices, offer opt-out options, and comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Seasonal and Campaign Visual Merchandising
Planning and Executing Campaigns
Thoughtful campaign planning prepares retailers for peak periods. A UK apparel retailer might schedule homepage updates before winter holidays based on previous sales data. Digital calendars should set clear objectives for each campaign period.
Large retailers often use template-based designs to launch updates quickly. This helps them respond to trends and inventory changes. Update frequency should be guided by customer data and retail calendars.
Unified campaign themes create memorable shopping experiences. Visual elements, messaging, and product selections should work together across all digital channels for consistency.
Measuring campaign effectiveness requires clear objectives and tracking metrics. These include click-through rates, conversions, and average order value. Analytics tools monitor the impact of content updates.
Teams that skip audience segmentation or regular tracking may miss chances for improvement. Adding a feedback loop where each campaign informs the next can help ensure progress based on actual performance.
Measuring Visual Merchandising Effectiveness
Key Metrics and Tracking Practices
Tracking digital merchandising means monitoring conversion rate, average order value, and cart abandonment. A fashion retailer might implement new 360 degree visuals and track changes in these metrics using analytics tools.
Comparing key metrics to industry benchmarks and historical data can help show true impact. Setting up custom segments and reviewing data over practical timeframes provides useful feedback.
Implementing Rigorous A/B Testing
A/B testing allows direct comparison of different visual merchandising styles. For clear results, each test should focus on a single feature, such as product image style. Sufficient sample size helps reduce random fluctuations.
Sales and engagement indicators tracked over appropriate periods can add reliability. Teams should determine sample size and test duration in advance to support actionable findings.
Attention Analytics and the Role of Attribution
Eye tracking and attention analysis can show how shoppers interact with digital displays. These tools highlight which elements attract attention and in what order. Attribution models help explain how various merchandising tactics contribute to conversion goals.
Retailers benefit when they view visual merchandising as a continuous practice. Using measured results as the foundation for improvement can create a cycle of steady growth.






























Continue reading…