Emerging technologies in OEM manufacturing: implications for suppliers
The landscape of original equipment manufacturing (OEM) is undergoing a transformative shift, driven largely by emerging technologies. These advancements are reshaping how OEM parts are designed, produced, and delivered. For suppliers, staying ahead of these trends is crucial not only for maintaining competitiveness but also for improving efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring high product quality.
This article will explore several key emerging technologies in OEM manufacturing and discuss their implications for suppliers in the industry. By understanding these innovations, suppliers can adapt to the changing market demands and capitalise on new opportunities.
1. The Role of Automation in OEM Manufacturing
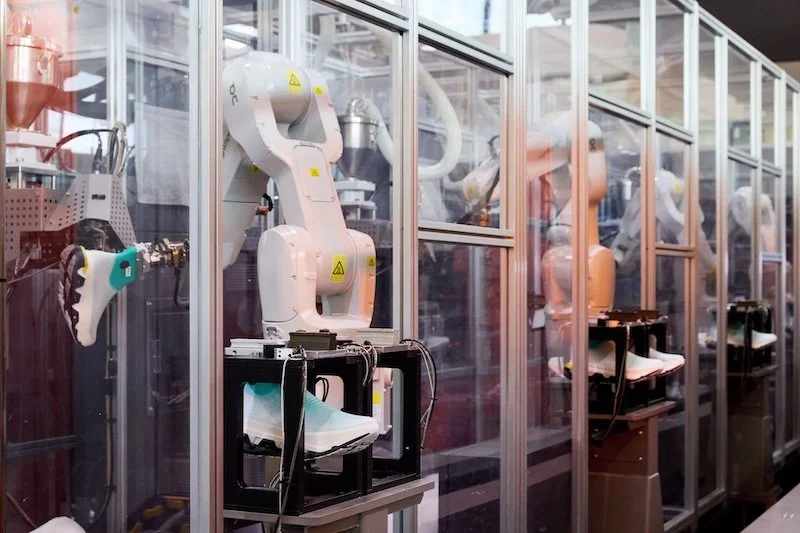
Automation has already made a significant impact in OEM manufacturing, and its role is expected to grow even more in the coming years. Automated systems streamline production processes, reduce human error, and improve precision, leading to enhanced efficiency and lower costs.
Robotic process automation (RPA), for instance, is increasingly used for tasks such as assembly, packaging, and quality control. For suppliers, adopting automation technologies not only boosts production speed but also reduces the risk of mistakes, allowing them to meet tight deadlines while maintaining high-quality standards.
OEM Source Inc. offers a comprehensive range of OEMS extensive inventory to help businesses streamline their production processes and maintain high standards of quality. With OEM’s extensive inventory of top-quality parts, OEM Source Inc. ensures that suppliers and manufacturers can access the components they need when they need them, all while maintaining cost-effectiveness and operational efficiency.
Whether you are looking for specific OEM components or need support in optimising your manufacturing processes, OEM Source Inc. provides the expertise and products to help you succeed in a competitive marketplace.
2. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) in OEM Production
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is another technology transforming OEM production. This technique allows manufacturers to produce components directly from digital models, reducing the need for traditional tooling and enabling rapid prototyping.
Suppliers can now create customized parts more quickly and cost-effectively, which significantly shortens lead times. The ability to produce small batches of complex components with minimal waste is a game-changer, especially in industries where demand for highly specialized parts is on the rise.
3. Internet of Things (IoT) in OEM Supply Chains
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionising the OEM supply chain by providing real-time data and insights into the performance of machines, equipment, and even components during production.
By integrating IoT sensors into production lines, manufacturers can monitor the health of their machinery, track inventory, and predict maintenance needs before a breakdown occurs. For suppliers, this means improved operational efficiency, reduced downtime, and more accurate demand forecasting, ultimately leading to lower operational costs and better customer service.
4. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Quality Control
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are beginning to play a central role in quality control within OEM manufacturing. These technologies enable manufacturers to detect defects in parts and products at an early stage by analyzing large amounts of production data.
AI algorithms can identify patterns and inconsistencies that might go unnoticed by the human eye, allowing suppliers to catch issues before they become costly problems. The adoption of AI powered quality control systems also helps suppliers ensure that products meet rigourous standards while reducing waste and the need for rework.
5. Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain technology, typically associated with cryptocurrencies, is gaining traction in OEM manufacturing due to its ability to provide transparent, secure, and immutable records of transactions.
In the context of OEM manufacturing, blockchain can be used to track the movement of parts and materials across the supply chain, ensuring authenticity and reducing the risk of fraud. Suppliers can use blockchain to create a more efficient and trustworthy supply chain, improving traceability, compliance, and customer confidence in the quality of OEM products.
6. The Shift Toward Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword in the OEM industry - it is a driving force behind many innovations. From reducing waste and energy consumption to using sustainable materials, OEM manufacturers are increasingly adopting green practices.
Technologies like energy efficient machinery, renewable energy sources, and closed-loop production systems are helping suppliers reduce their environmental footprint. Suppliers that embrace sustainable manufacturing practices not only contribute to environmental conservation but also meet growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products, gaining a competitive advantage in the market.
7. Collaborative Robots (Cobots) in OEM Production
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed to work alongside human operators in the manufacturing process. Unlike traditional robots, which are often confined to a specific task or area, cobots are flexible and adaptable, assisting workers with repetitive or physically demanding tasks.
In OEM manufacturing, cobots can handle tasks such as lifting heavy parts, performing quality inspections, or assembling components, all while working safely alongside humans. The use of cobots can help suppliers increase productivity, improve worker safety, and reduce the physical strain on employees.
8. Augmented Reality (AR) for Design and Maintenance
Augmented reality (AR) is emerging as a valuable tool in OEM manufacturing for both design and maintenance. With AR, manufacturers can visualise 3D models of components and products during the design phase, allowing for more accurate prototypes and faster iterations.
On the maintenance side, AR enables technicians to overlay digital information onto physical machines, providing real-time guidance for repairs or upgrades. For suppliers, this technology helps reduce errors in both design and maintenance, leading to higher-quality products and more efficient operations.
9. Advanced Materials for OEM Parts
The development of advanced materials is another area of innovation in OEM manufacturing. Materials like lightweight composites, smart materials, and biodegradable plastics are changing the way components are designed and produced.
These materials offer improved performance characteristics, such as higher strength, better heat resistance, and enhanced durability. Suppliers who embrace these advanced materials can offer OEM parts that are lighter, stronger, and more sustainable, meeting the increasing demands for high-performance and eco-friendly products in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
10. The Future of OEM Manufacturing: Integrated Systems and Smart Factories
Looking ahead, the future of OEM manufacturing will be defined by integrated systems and smart factories. These advanced manufacturing environments are connected through a network of IoT devices, AI powered machines, and automated processes that work together seamlessly to optimize production.
For suppliers, smart factories offer enhanced efficiency, reduced costs, and the ability to quickly adapt to changes in demand or product design. The integration of these technologies allows for more flexible, agile, and scalable manufacturing operations, positioning suppliers to thrive in an increasingly competitive global market.
Conclusion
Emerging technologies are reshaping OEM manufacturing and offering suppliers new ways to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and meet growing customer demands for high quality products. From automation and 3D printing to AI powered quality control and sustainable practices, these innovations are driving the industry toward a more advanced, interconnected future.
Suppliers who embrace these technologies will not only remain competitive but will also be better equipped to navigate the challenges and opportunities of an ever changing market.






























Continue reading…